OF TERMS

Click any Term for Definition:
TANGO2 deficiency disorder
TANGO2 deficiency disorder is a gene responsible for performing a specific job in the body which is actually the acronym it stands for — Transport And Golgi organization.
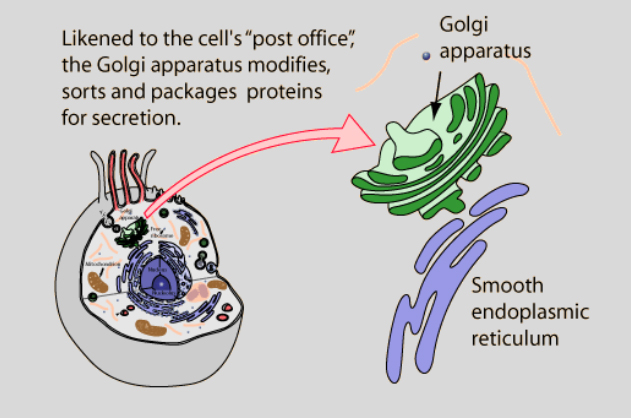
Golgi
Golgi functions as a factory in which proteins received from the endoplasmic reticulum are processed and sorted for transport to their eventual destinations.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Endoplasmic reticulum is a collection of tubes that make, package, and transport proteins and fats.
Exons
An exon is a coding region of a gene that contains the information required to encode a protein.
Deletion
A genetic deletion means that a part of a chromosome is missing. A very small piece of a chromosome can contain many different genes. When genes are missing, there may be errors in the development of a baby, since some of the “instructions” are missing.
Misspelling
A misspelling is a change or mutation in a gene.
Variants
A variant is a permanent change in the DNA sequence that makes up a gene
Autosomal Recessive
This is a condition inherited from both parents that results from having no functioning copies of a gene.
Mitochondria
Mitochondria are the parts of our cells that generate energy from food that the rest of the cell can use.
Metabolism
Metabolism is all the chemical reactions involved in converting food into energy.
Metabolomics
Metabolomics is the study of small molecules, known as metabolites, within cells, biofluids, tissues or organisms.
Recurrent Metabolic Crises
Our body has an order or a way that it works best to give us energy and keep us healthy. When the TANGO2 gene doesn’t work in the body, it disrupts this order and it causes a crisis because we can’t utilize this typical way of making energy. We can measure metabolic crisis with lab tests. The body uses up all of its sugar resulting in low blood sugar which leads to hypoglycemia. There can be a build up in lactic acid called lactic acidosis. Lactate and glucose are closely related and so a decrease in one can cause an increase in another. We can also see elevated ammonia called hyperammonemia.
Enzyme
An enzyme is a protein molecule in cells that speeds up chemical reactions in the body, but does not get used up in the process. Therefore it can be used over and over again.
Fatty Acid Oxidation
During digestion the body breaks down fats into fatty acids which can then be absorbed into the blood. Fatty acids have many important functions in the body, including energy storage. If glucose (a type of sugar) isn’t available for energy, the body uses fatty acids to fuel the cells instead.
Membrane Traffic
Membrane trafficking is the process by which proteins and other macromolecules are distributed throughout the cell.
Carnitine
Carnitine is a natural substance that the body uses to process fats and produce energy. Carnitine deficiency is when not enough (less than 10%) of the nutrient carnitine is available to cells in the body. This can cause muscle weakness and heart or liver problems.
Rhabdomyolysis
This is the breakdown of muscle. With TANGO2 there can be muscle injury from all the abnormal labs of a metabolic crisis that cause the muscle fibers to die and break down. Muscle that breaks down releases myoglobins which can attack the kidneys. A healthy kidney filters waste, but a kidney that is being attacked can’t filter out water and toxins and it can cause changes in urine color and make a child very sick. We measure how much muscle is breaking down by measuring Creatine kinase or CK.
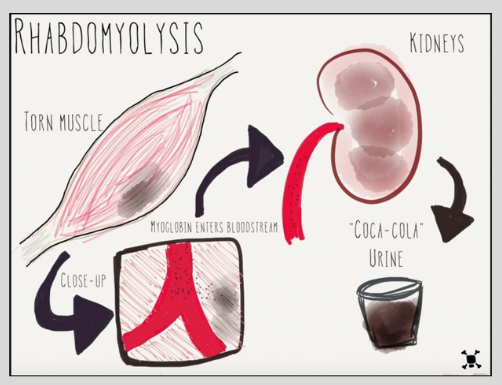
Myoglobins
Myoglobin is a protein found in heart tissue and other muscles. It is released into the blood after damage to the heart or other muscles. It can be checked with a blood test or a urine test.
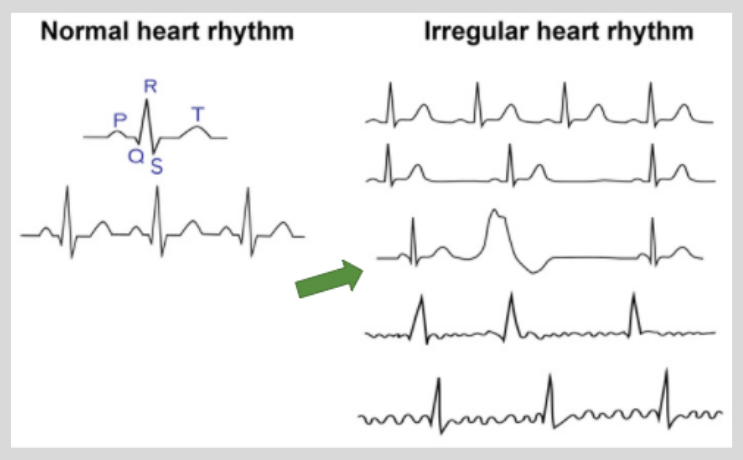
Cardiac Arrhythmias
An arrhythmia is any change in heart rhythm. Hearts typically have a very specific wave and the PQRST describes the normal shape of that wave. With arrhythmia related to TANGO2, the most common change is an increase in space between the Q and T part of the wave called QT prolongation. Any change to our normal heart wave is dangerous because it may not snap back into normal rhythm and the heart can stop.
Tachycardia
Tachycardia is an abnormally fast heart rate.
Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy is when the heart muscle becomes weak and enlarged, which makes it difficult to pump blood through the body.
Myocytes
These are a type of cell found in muscle tissue. They develop from myoblasts to form muscles in a process called myogenesis.
Encephalopathy
This is damage to the brain that changes the firing patterns of the mind. Our brain activity is measured in waves. An EEG is an electroencephalogram which measures the electrical impulses of the brain. EEGs are supposed to show minimal peaks but with encephalopathy, there are peaks and lows that don’t follow a normal pattern. This is an indication that the brain is not functioning correctly. This often can explain delays and issues in learning.
Biomarker
This is a biological molecule found in blood, other body fluids, or tissues that is a sign of a normal or abnormal process, or of a condition or disease. A biomarker may be used to see how well the body responds to a treatment for a disease or condition.
Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSC)
These cells are master cells. They are able to make cells from all three basic body layers, so they can potentially produce any cell or tissue the body needs to repair itself. This “master” property is called pluripotency.
Fibroblast
A fibroblast is a cell that forms connective tissue fibers.
Skin fibroblasts form skin cells.
Pathophysiology
This is changes in the body associated with a particular disease or injury, or the study of such changes.
CRISPR
CRISPR is a technology that can be used to edit genes.

